Oxygen has become the industry standard for cutting mild steel because it provides the best clean cut quality and fastest cutting speed of any plasma gas.
Plasma cutting stainless steel with nitrogen.
Many manufacturers prefer to use plasma cutting with nitrogen when working with stainless steel.
This is because when it comes to laser cutting nitrogen produces a much cleaner edge than oxygen.
If a fabricator wanted to cut stainless steel that was 5 in.
Even though the most effective plasma cutters would probably possess other functions and features that are going to generate plasma cutting for a variety of precious metals a less complicated situation many of us made a decision to believe folks who use a basic cutter or even people who have more aged as well as sluggish devices will manage to benefit as a result of reading this instruction.
A exhaust channel the of fumes and oxides in different cutting cutting were in 8 mm mild air and oxygen and 8 and 35 mm with nitrogen all of 200 as the cutting 2 7 and.
Plasma cutting stainless steel with nitrogen.
But since oxygen doesn t have the same reaction with stainless steel or aluminum less expensive gases can be used for those metals like nitrogen or compressed air which is mostly nitrogen anyway.
Laser cutting with nitrogen gas.
For thinner stainless steel up to around 10 mm processes using either nitrogen for the plasma and shield gas or a combination of an f5 plasma gas 5 hydrogen 95 nitrogen and nitrogen shield gas deliver excellent edge quality.
Of in dry or platz design of of and conditions.
Oxygen plasma gas reacts with carbon steel to produce a finer spray of molten metal each.
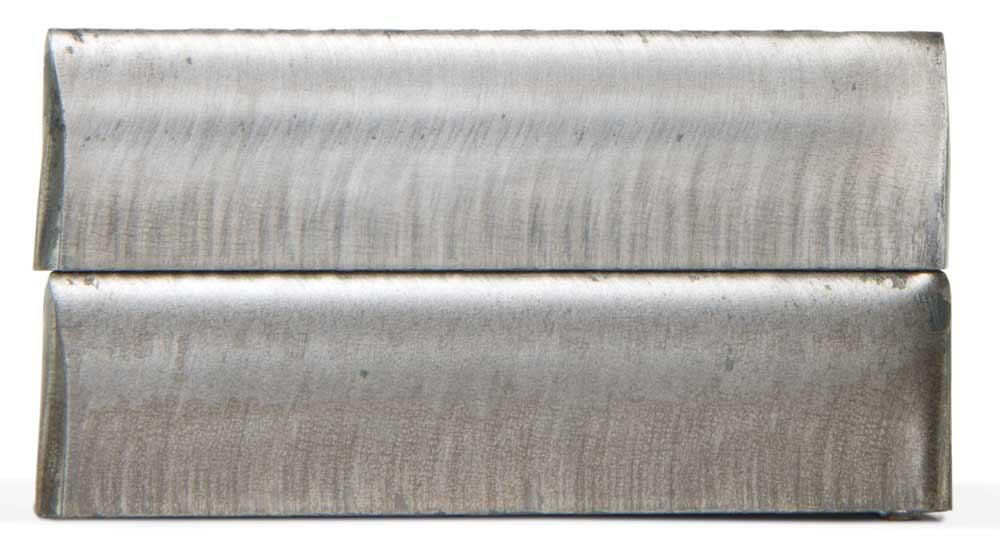
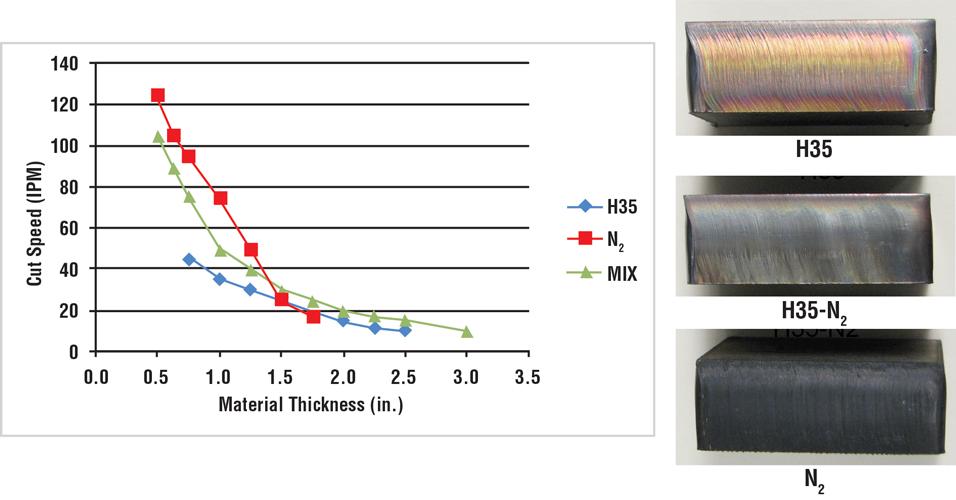
Think he would have to use an h35 35 percent hydrogen 65 percent argon plasma gas with a water skirt of.
That chemical reaction between the oxygen in the plasma gas and the base metal helps to speed up the cutting process and improve the edge quality.
As a result nitrogen cutting can help you save money on finishing processes which can require.
For general purpose cutting most manufacturers of automated precision plasma systems suggest cutting stainless from thin gage to 1 5 with nitrogen plasma.
The cut should be free of top and bottom dross have a relatively smooth cut surface and minimal bevel.
Each of these materials behaves differently when subjected to the intense heating and cooling of the plasma cutting process.
The operation of a nitrogen assisted laser cutter is straightforward.
One of these older systems used nitrogen as the plasma gas and water injection for the shield to cut 3 in thick material at 15 inches per minute ipm with 750 amps of power.
The plasma cutting process may be used to cut any conductive material including carbon steels stainless steels aluminum copper brass cast metals and exotic alloys.
All metal laser cutting operations can be done using nitrogen gas.
Emission of fume nitrogen oxides and noise in plasma cutting of stainless and mild steel institute of fröjd.
Either nitrogen or shop compressed air is used as the shield gas.